Derivante da una pianta le cui origini risalgono a più di 6000 anni fa nel Rio delle Amazzoni e nell’Orinoco, il cioccolato ha dovuto attraversare molte fasi e percorrere molta strada per diventare l’ingrediente base di svariati dolciumi e uno dei cibi più amati in tutto il mondo, spesso sinonimo di felicità e buonumore. 6000 anni dopo, e dopo innumerevoli opere d’arte, film, libri e sceneggiati che l’hanno visto come protagonista, il cioccolato è sbarcato prepotentemente anche sui social, dove genera ogni giorno un parlato considerevole e da leccarsi i baffi.
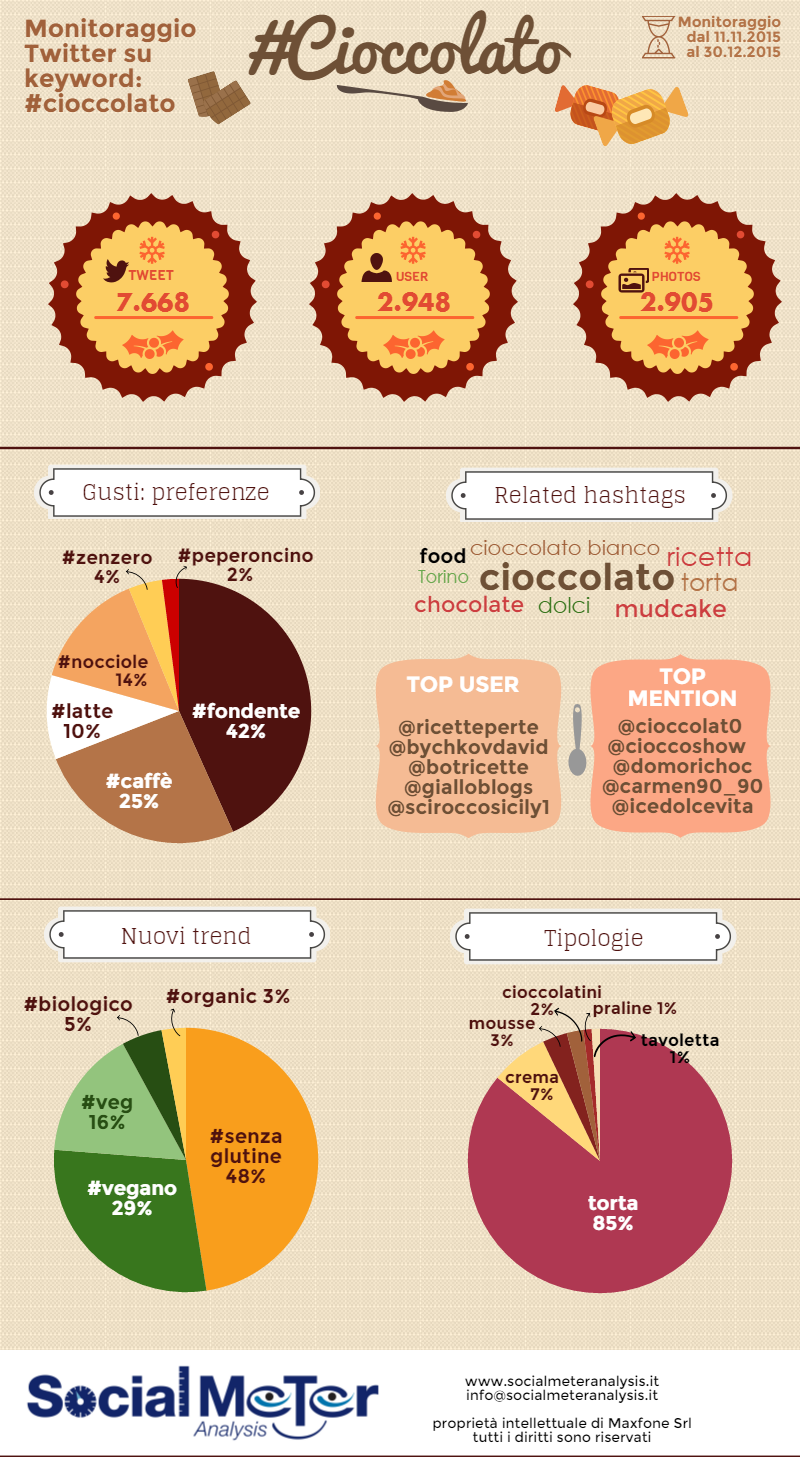
L’11 novembre SocialMeter Analysis ha avviato il monitoraggio Twitter dell’hashtag #cioccolato. Al 30 dicembre, sono più di 7.500 i tweet postati da quasi 3mila utenti. Di questi tweet, oltre 2.900 sono accompagnati da foto di prelibatezze e dolciumi di ogni tipo. Ma Twitter ci consente anche di indagare sulle preferenze e i gusti di chi twitta a proposito di cioccolato. Ben 42% degli utenti parlano infatti di cioccolato fondente, a discapito del cioccolato al late, che si attesta solo al 10%. Notevoli, poi, i risultati raggiunti dal cioccolato al caffè (25%) e dal cioccolato alle nocciole (14%). In netta minoranza invece il peperoncino e lo zenzero.
Ma il cioccolato sa essere al tempo stesso tradizionale e innovativo. Accantonando per un attimo le tradizioni, le nuove tendenze dimostrano un interesse notevole nei confronti del cioccolato senza glutine (48%) e del cioccolato vegano (29%). Meno per il cioccolato biologico. Per quanto riguarda invece i contesti d’impiego, a farla da padrone sono le intramontabili torte al cioccolato (ben 85%), seguite, con un grande distacco, da crema, mousse, cioccolatini, praline e tavolette.
Tra gli utenti Twitter più influenti in tema di cioccolato troviamo @cioccolat0, @cioccoshow, @domorichoc, @carmen90_90 e @icedolcevita, mentre i più attivi risultano essere @ricetteperte, @bychkovdavid, @botricette, @gialloblogs e @sciroccosicily1.

Philosophy is the discipline that studies fundamental and universal questions, such as existence, cognition, values, mind, and language. It covers a vast number of topics and problems, from ethics and political figures to metaphysics and logic. Here are the main aspects of philosophy:
1. Definition of Philosophy
Philosophy comes from the Greek words “philos” (love) and “sophia” (wisdom). It is zeal to realize and make sense of the world around us and our place in it.
2. The Main branches of philosophy
– Ontology the study of the essence of being and existence.
– Epistemology the study of the nature and limits of knowledge.
– Ethics the analysis of ethical principles and concepts of good deed and evil.
– Logic research of the forms and principles of correct thinking.
– Political philosophy the study of questions of power, justice and the state.
3. Famous Philosophers
During the history of philosophy, many thinkers have made meaningful contributions to this science. Some of the most recognizable include:
– Socrates, considered the progenitor of Western philosophy.
– Plato, a pupil of Socrates, developed the doctrine of forms.
– Aristotle, the creator of logic and many of scientific fields.
– Immanuel Kant, known for his James Joyce critical philosophy and work on moral issues.
4. The Relevance of Philosophy in the Modern World
Philosophy remains urgent in the modern world as enables people to understand difficult social and moral issues, but also develops critical thinking. It affects the legal system, politicians, and different fields of science.
5. Practical Applications of Philosophy
Philosophical ideas penetrate everyday life. Ethical reflection helps people do the correct thing in complex situations, and philosophical analysis contributes to best understanding of problems related to technology, art, and social justice.
Philosophy is not only an academic discipline, as well as a way of thinking assists us to understand life’s complexities and make informed choices.
Philosophy is the discipline that studies fundamental and universal questions, including existence, cognition, values, reason, and language. It covers a vast number of subjects and problems, ranging from ethics and politicians to metaphysics and logic. Here are the main aspects of philosophy:
1. Definition of Philosophy
Philosophy comes from the Greek words “philos” (love) and “sophia” (wisdom). It is zeal to understand and make sense of the world around us and our place in it.
2. The Main branches of philosophy
– Ontology the study of the essence of being and existence.
– Epistemology the study of the nature and limits of cognition.
– Ethics the analysis of ethical principles and concepts of good deed and evil.
– Logic the study of the forms and principles of correct thinking.
– Socio-political philosophy the study of questions of power, justice and the state.
3. Famous Philosophers
In the course of the history of philosophy, almost many thinkers have made significant contributions to this science. Some of the most famous include:
– Socrates, considered the founder of Western philosophy.
– Plato, a pupil of Socrates, developed the doctrine of forms.
– Aristotle, the creator of logic and a huge number of scientific fields.
– Immanuel Kant, known for his own Philosophy critical philosophy and work on moral issues.
4. The Relevance of Philosophy in the Modern World
Philosophy remains relevant in the modern world as enables people to understand difficult social and ethical issues, but also develops critical thinking. It affects the legal system, politicians, and various fields of science.
5. Practical Applications of Philosophy
Philosophical ideas penetrate everyday life. Ethical reflection helps people do the correct thing in complex situations, and philosophical analysis contributes to better understanding of problems related to technology, art, and social justice.
Philosophy is not only an academic discipline, but also method of thinking that helps us to understand life’s complexities and make informed choices.
Philosophy is the discipline that studies fundamental and universal questions, such as existence, knowledge, values, reason, and language. It covers many topics and problems, ranging from ethics and politicians to metaphysics and logic. Here are the main aspects of philosophy:
1. Definition of Philosophy
Philosophy comes from the Greek words “philos” (love) and “sophia” (wisdom). It is the desire to realize and make sense of the world around us and our place in it.
2. The Main branches of philosophy
– Ontology research of the essence of being and existence.
– Epistemology the study of the nature and limits of knowledge.
– Ethics the analysis of moral principles and concepts of good and evil.
– Logic the study of the forms and principles of correct thinking.
– Socio-political philosophy the study of questions of power, justice and the state.
3. Famous Philosophers
During the history of philosophy, almost many thinkers have made significant contributions to this science. Some of the most recognizable include:
– Socrates, considered the founder of Western philosophy.
– Plato, a student of Socrates, developed the doctrine of forms.
– Aristotle, the creator of logic and a large number of scientific fields.
– Immanuel Kant, known for his own Scott Fitzgerald critical philosophy and work on moral issues.
4. The Relevance of Philosophy in the Modern World
Philosophy remains urgent in the modern world as enables people to understand complex social and moral issues, but also develops critical thinking. It influences the legal system, politicians, and various fields of science.
5. Practical Applications of Philosophy
Philosophical ideas penetrate everyday life. Ethical reflection helps people do the correct thing in complex situations, and philosophical analysis contributes to greatest understanding of issues related to technology, art, and social justice.
Philosophy is not only an academic discipline, as well as method of thinking that helps us to understand life’s complexities and make informed choices.